How to make simple astrolabe, Science Fair Projects
Introduction
A Simple Astrolabe
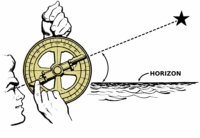
The astrolabe is an ancient device, long used to measure latitude and act as an aid to navigation. Historians believe that the first astrolabes were devised by the Ancient Greeks, with astronomers such as Apollonius (c. 262 BCE – c. 190 BCE) and Hipparchus (190 BCE – c. 120 BCE) developing the theory behind the device.
Using an Astrolabe
Although there is a lot of debate about who built the first astrolabe, the consensus is that Hipparchus has that honor, using it as a much more accurate way of measuring latitude than a gnomon.
The astrolabe is an instrument that allows observers to measure the position of celestial bodies relative to the horizon, which allows accurate star mapping. The utility of the instrument does not end there,  because it can be used to measure latitude, give the local time and estimate the height of objects; astrolabes were used by surveyors for measuring distance through triangulation. The standard astrolabe consists of a disc with a rotating arm complete with sights, but quadrants, sextants and inclinometers all use the same principle.
because it can be used to measure latitude, give the local time and estimate the height of objects; astrolabes were used by surveyors for measuring distance through triangulation. The standard astrolabe consists of a disc with a rotating arm complete with sights, but quadrants, sextants and inclinometers all use the same principle.
Build a Clinometer – A Simple Astrolabe
Blume Clinometer
A clinometer based upon same principles as the protractor device (Public Domain) With a few simple items, you can build your own simple astrolabe and start to chart the motion of the stars. This particular version is usually referred to as a clinometer or inclinometer, and can also be used to measure height using trigonometry. Foresters often use clinometers to measure the height of trees and this device can measure latitude from the star Polaris, although navigators and astronomers use much more complex instruments.
You will need:
- A protractor: Try to find one that has a small hole halfway along the straight edge

- A plastic drinking straw
- Strong sticky tape
- String or fishing twine
- A fishing weight
To build the protractor:
- Simple Clinometer
- Simple Clinometer (Public Domain)
- Using sticky tape, carefully attach the drinking straw along the straight edge of the protractor. This will act as a sighting guide for looking at stars and planets.
- Tie the fishing weight to one end of the string
- Feed the other end of the string through the hole in the protractor and use a knot or small piece of sticky tape to hold it in place
- Hold the protractor, curved side down, and look at the intended star through the straw
- Press the string tightly against the side of the protractor and carefully lower it, noting which degree mark the string passes through. Alternatively, you can ask a friend or classmate to read the angle
- Take measurements of several stars every half-an hour
- This will allow you to guess at how the stars rotate around the sky
- You can also use your inclinometer to guess the height of trees and structures, using triangulation.
The Ocean Service provides a great version of this use of an astrolabe.Of course, this is a very simple astrolabe, and ancient astronomers and mariners used much more elaborate devices, usually disc or wheel shaped, and often engraved with the positions of the stars. Even in the modern world, aircraft use inclinometers to measure banking angle, showing that the knowledge of the ancients still touches modern life in many ways.






